Sample Questions: Principles of Microeconomics
The following Principles of Microeconomics sample questions aren't used in actual CLEP exams and aren’t presented here exactly as they will be on the test. Use them to get a sense of question format and difficulty level.
Directions
An online scientific calculator will be available for the questions on this test. For each question, select the best of the choices given. Some items refer to figures—insert those images where noted.
Questions
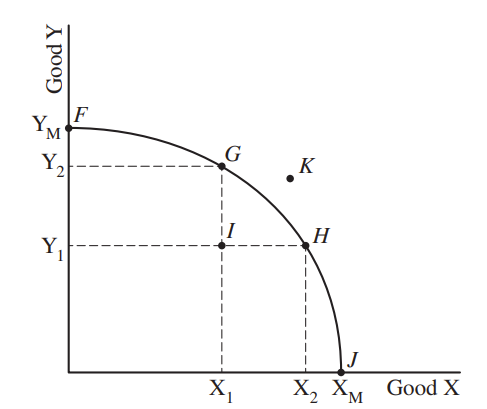
Graph referenced in Question 1 showing point I on a production possibilities curve.
1. Which of the following is true if the country is producing at point I?
- The country can increase the production of Good X only by decreasing the production of Good Y.
- The country is producing the efficient combination using all its available resources.
- The country can produce more of both goods with its existing resources.
- The country cannot increase the production of either good.
- The country’s level of unemployment will not change by moving from point I to point H.
Suppose that oranges and apples are close substitutes. If the price of apples decreases, the equilibrium price and quantity of oranges are expected to change in which of the following ways?
Equilibrium Changes in the Orange Market Price of Oranges Quantity of Oranges A. Increase Increase B. Increase Decrease C. No change Decrease D. Decrease Increase E. Decrease Decrease - When the price of a product increases, a consumer’s real income decreases, causing the consumer to decrease the quantity of the product demanded. This is known as:
- The substitution effect
- The income effect
- Income elasticity
- Cross-price elasticity
- Diminishing marginal utility
- Assume that a firm is producing 1,000 units of output using both labor and capital. The last unit of labor used has a marginal product of 80 units of output; the last unit of capital used has a marginal product of 50 units of output. If the unit price of labor is $16 and the unit price of capital is $5, which of the following statements is true?
- The firm should be able to produce more than 1,000 units with the labor and capital currently being used.
- The firm is minimizing the total cost of producing 1,000 units of output.
- The firm should use more capital and less labor to reduce the total cost of producing 1,000 units.
- The firm should use less capital and more labor to reduce the total cost of producing 1,000 units.
- Since the price of capital is less than the price of labor, the firm should produce using all capital and no labor.
- A profit-maximizing firm will shut down in the short run if:
- Marginal cost is greater than average total cost
- Marginal cost is equal to average total cost
- Price is less than average total cost
- Price is less than average variable cost
- Average variable cost is greater than average fixed cost
- Which of the following is true of the marginal factor cost for a firm hiring labor in a perfectly competitive labor market?
- It is constant and equal to the market wage rate.
- It is greater than the market wage rate.
- It is less than the market wage rate.
- It increases as the number of workers hired increases.
- It decreases as the number of workers hired increases.
- In a competitive market, when a negative externality exists, the private market produces:
- More than the socially optimum level because the marginal social cost is less than the marginal private cost
- More than the socially optimum level because the marginal social cost is greater than the marginal private cost
- Less than the socially optimum level because the marginal social benefit is less than the marginal private benefit
- Less than the socially optimum level because the marginal private benefit is greater than the marginal external cost
- The optimal level of output because marginal private benefits equal marginal social costs
The table below shows ABC Farming’s total cost of producing various quantities of corn. The market for corn is perfectly competitive, and the market price for corn is $10 per bushel. What is ABC Farming’s profit-maximizing quantity?
ABC Farming — Total Cost of Corn Production Bushels of Corn Total Cost ($) 0 $20 1 $25 2 $32 3 $41 4 $52 5 $65 - 1 bushel
- 2 bushels
- 3 bushels
- 4 bushels
- 5 bushels
Answers
1) C 2) E 3) B 4) C 5) D 6) A 7) B 8) C